The Zika virus (ZIKV) is a flavivirus related to Dengue, Yellow Fever virus, Japanese encephalitis virus and West Nile virus. It is responsible for mosquito-transmitted infection known as Zika fever or Zika disease.
Zika Virus is commanding worldwide attention recently because researchers have found evidence that Zika may be linked to birth defects and neurological conditions like microcephaly and Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults.
Systematic classification of Zika virus
- Group: Group IV ((+)ssRNA)
- Family: Flaviviridae
- Genus: Flavivirus
- Species: Zika virus
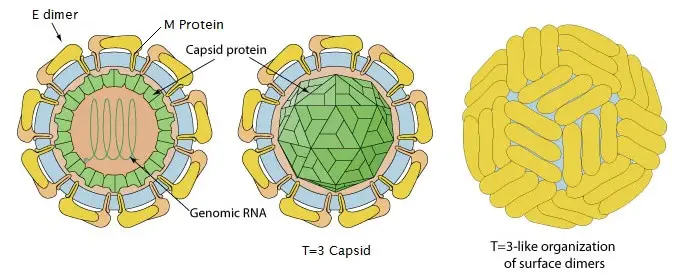
Structure of Zika virus
Zika virions are typically icosahedral-shaped. They are enveloped, 18-45 nanometer in diameter.
The genome is a positive strand RNA enclosed in a capsid and surrounded by a membrane. The RNA contains 10,794 nucleotides encoding 3,419 amino acids.
The virus is inactivated by ether, sodium dexoxycholate and chloroform.
Epidemiology
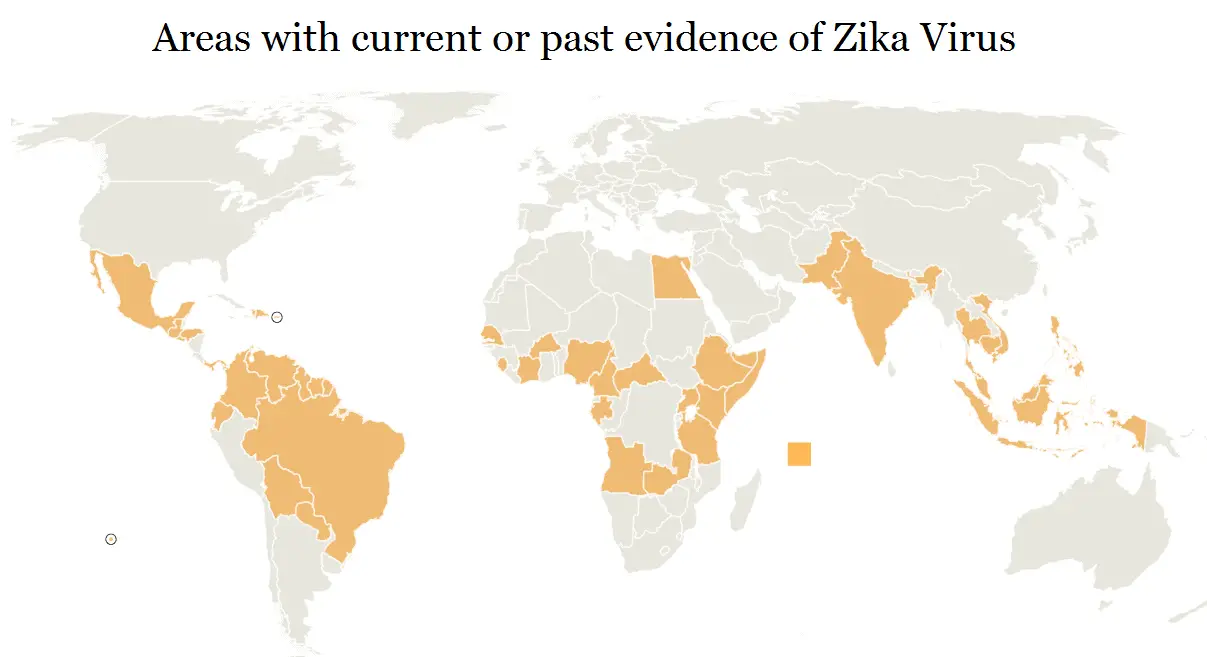
- Zika virus was first isolated in 1947 from the blood of a Rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) in Zika forest, near Entebbe in Uganda. Subsequently, the virus was recovered from humans and mosquitoes in Uganda, Senegal, Nigeria, Ivory Coast, the Central African Republic and Malaysia.
- In 2007, a large outbreak of Zika virus infection occured in Yap Island of Micronesia, where nearly 75% of the population was infected.
- Zika virus did not begin spreading widely in the Western Hemisphere until last May 2015, when the public health authorities of Brazil confirmed an outbreak in northeast Brazil.
According to WHO, since Brazil reported the first cases of local transmission, Zika virus has spread to 21 countries and territories of the Americas. The WHO estimates 3 million to 4 million people across the Americas will be infected with the virus in the next year.
Pathogenesis of Zika virus
Transmission :
Zika virus spreads to people through mosquito bites. The virus was recovered from mosquitoes of Aedes genus including Aedes africanus, Aedes apicoargenteus, Aedes leuteocephalus, Aedes aegypti, Aedes vitattus and Aedes furcifer.
Some evidence suggest that Zika virus can also be transmitted to humans through blood transfusion, perinatal transmission and sexual transmission. However these modes are very rare. The virus was found on one occasion in semen.
The disease cycle continues as Resorvoir host to mosquito to reservoir host; 2-5 days viremia in host, 5-7 days in mosquito, then back to the host.
Information regarding pathogenesis of ZIKV is scarce but mosquito-borne flaviviruses are thought to replicate initially in dendritic cells near the site of inoculation then spread to lymph nodes and the bloodstream. Although flaviviral replication is thought to occur in cellular cytoplasm, One study suggested that ZIKV antigens could be found in infected cell nuclei.
Incubation Period :
The incubation period (the time from exposure to appearance of symptoms) of Zika virus disease is not clear, but is likely to be 3-12 days.
Signs and Symptoms :
About only 20-25% of people infected with Zika virus develop symptoms. The most common symptoms of Zika virus infection are:
- Fever
- Maculopapular rashes
- Joint pain (arthritis, arthralgia)
- Conjunctivitis(red eyes)
- Muscle pain
The zika infection is more serious as it is associated with two neurological conditions:
- Microcephaly : A serious birth defect in which babies have small heads and incomplete brain development. This may occur when mother gets infected during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome : Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) is a rare disorder where a person’s own immune system damages the nerve cells, causing muscle weakness and sometimes, paralysis.
Laboratory diagnosis of Zika virus
There is no widely available test for Zika infection. In most people, diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and epidemiological circumstances (such as Zika outbreak in the patient’s area or trips to areas where the virus is circulating).
Diagnostic tests for ZIKV infection include :
- Polymersase Chain Reaction – Nucleic acid detection by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) targeting the non-structural protein 5 genomic region is the primary means of diagnosis. It is useful in the first 3-5 days after the onset of symptoms.
- Serological Tests – An ELISA has been developed to detect IgM to ZIKV only after five days. Because it is closely related to dengue and yellow fever, it may cross-react with antibody tests for those viruses.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test – Nucleic acid amplification test (NAT) for detection of viral RNA can also be performed.
- Plaque Reduction Neutralization Assay – The Plaque reduction neutralization assay generally has improved specificity over immunoassays, but may still yield cross-reactive results in secondary flavivirus infections.
Treatment of Zika virus
No specific vaccine or medications are available to prevent or treat ZIKA virus infections. The symptoms are mild – when they appear at all – and usually require only rest, nourishment and other supportive care.
Prevention and control of Zika virus
- Elimination and control of mosquito : Avoid allowing standing water in outdoor containers so that they do not become mosquito breeding sites, avoid accumulating garbage, use mosquito nets in windows and doors.
- Prevention of mosquito bites : Personal protection measures to avoid mosquito bites should be applied when staying in risk areas, sleep under mosquito nets, do not travel in affected areas.
- Public awareness about Zika and mosquitoes : Peoples should be made aware about the disease and it’s preventive measures. They should take the basic precautions to protect themselves from the disease.

thank u for the great information
Great information, it feels like studying all over again after reading each article.
excellent
Thanks for this useful information at least it helps me out during my seminar presentation. Thanks so much
Thanx alot…. For this useful information …. It help me in my annual exam prepration…
The reproductive cycle of the Zika virus in the receptors cell?