Papanicolaou stain (also Papanicolaou’s stain or PAP stain) is the most important stain utilized in the practice of Cytopathology. It is a polychromatic stain containing multiple dyes to differentially stain various components of the cells.
This technique was developed by George Papanicolaou, the father of Cytopathology. This method is used to differentiate cells in the smear preparation of various gynecological specimens (pap smears), materials containing exfoliative cells and material from fine needle aspiration.
Objectives of Papanicolaou stain
Papanicolaou described three chief objectives for staining of cytological smears:
- Definition of nuclear details : Because of the widespread muclear abnormalities of cancer cells and their diagnostic significance, good staining of the nucleus is of primary importance.
- Transparency of cytoplasm : This is of particular importance because of the varying thickness and the frequent overlapping of cells.
- Differentiation of cells : Differences in the staining reaction such as that between acidophilic and basophilic cells help greatly in the identification of certain cell types found in smears.
Principle of Papanicolaou stain
Papanicolaou stain includes both acidic and basic dyes. Acidic dye stains the basic components of the cell and basic dye stain the acidic components of the cell.
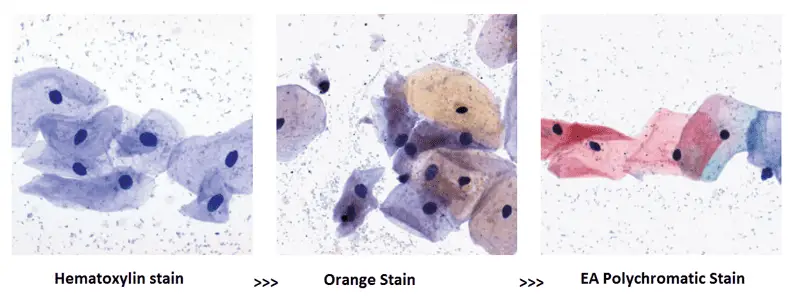
The polychromatic PAP stain involves five dyes in three solutions.
- Hematoxylin : Natural dye hematoxylin is the nuclear stain which stains cell nuclei blue. It has affinity for chromatin, attaching to sulphate groups on the D.N.A. molecule. Harris’ hematoxylin is the commonest cytologically although Gills’ hematoxylin and Hematoxylin S can be used.
- Orange Green 6 : This is the first acidic counterstain (cytoplasmic stain) which stains matured and keratinized cells. The target structures are staine d orange in different intensities.
- Eosin Azure : This is the second counterstain which is a polychrome mixture of eosin Y, light green SF and Bismarck brown. Eosin Y gives a pink colour to cytoplasm of mature squamous cells, nucleoli, cilia and red blood cells. Staining solutions commonly used in cytology are EA 31 and EA 50, while EA 65
- Light green SF stains blue to cytoplasm of metabolically active cells like parabasal squamous cells, intermediate squamous cells and columnar cells.
- Bismarck brown Y stains nothing and sometimes it is often omitted.
Composition and preparation of reagents
- Harris’ hematoxylin :
Hematoxylin = 5g
Ethanol = 50ml
Potassium alum = 100g
Distilled water (50°C) = 1000ml
Mercuric oxide = 2-5g
Glacial acetic acid = 40ml - Orange G 6 :
Orange G (10% aqueous) = 50ml
Alcohol = 950ml
Phosphotungstic acid = 0-15g - EA 50 :
0.04 M light green SF = 10ml
0.3M eosin Y = 20ml
Phosphotungstic acid = 2g
Alcohol = 750ml
Methanol = 250ml
Glacial acetic acid = 20ml
Filter all stains before use.
Procedure of Papanicolaou staining
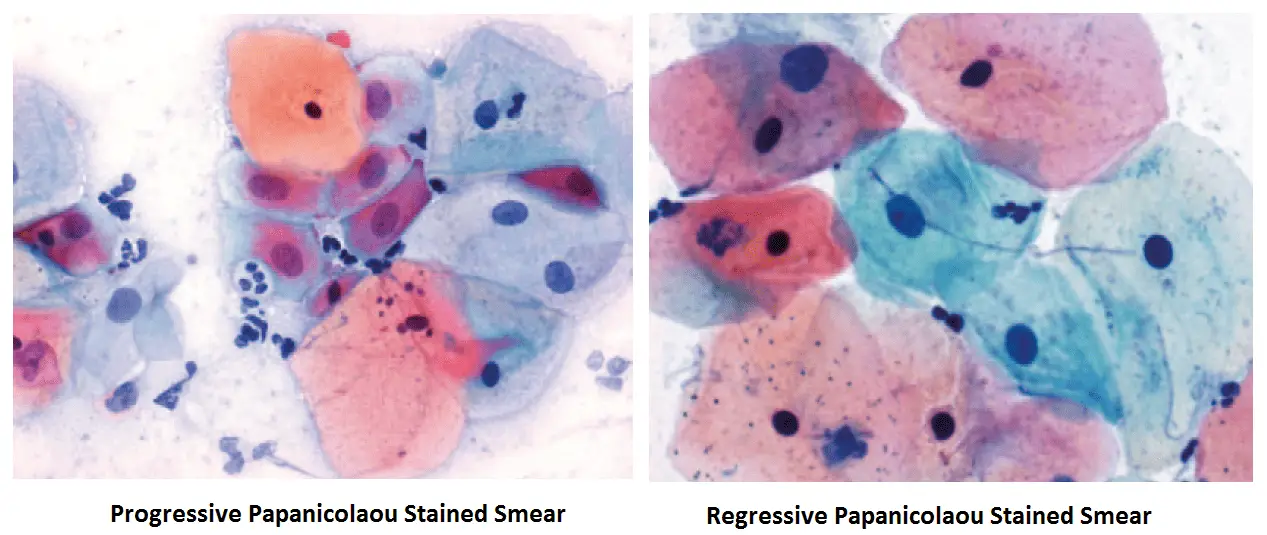
Both progressive and regressive nuclear staining techniques can be used in Papanicolaou stain. Before staining, Wet fixation immediately with Cytology spray fixative 96% ethanol for minimum 30 min is required.
Procedure of Progressive Papanicolaou Staining Method
In the progressive method, the nucleus is stained with hematoxylin to a intensity desired. The intensity of the nuclear staining is controlled by the immersion of the slide into a blueing agent. Most commonly used blueing agent is Sott’s tap water (pH 8.02).
2.80% Alcohol2 minutes
| Step | Reagent | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 95% Alcohol (Fixation) | 15-30 minutes |
| 3. | 60% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 4. | Distilled Water | 5 dips |
| 5. | Distilled Water | 5 dips |
| 6. | Hematoxylin stain | 3 minutes |
| 7. | Distilled Water | 3 minutes |
| 8. | 60% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 9. | 80% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 10. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 11. | Orange G Stain | 3 minutes |
| 12. | 95% ALcohol | 2 minutes |
| 13. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 14. | Eosin Azure Stain | 3 minutes |
| 15. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 16. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 17. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 18. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 19. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 20. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 21. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 22. | Absolute Alcohol+Xylene (1:1) | 2 minutes |
| 23. | Xylene | 2 minutes |
| 24. | Xylene | 2 minutes |
| 25. | Xylene | Till clear |
| 26. | Mount in D.P.X |
Procedure of Regressive Papanicolaou Staining Method
When using the regressive staining method, the nucleus is deliberately over-stained with a non-acidified haematoxylin. The excess stain is removed with dilute hydrochloric acid solution (acid water).
The decolourising process is then stopped by immersing the slide in running tap water. Timing is crucial in the regressive method as de-staining may lead to a hyperchromatic nucleus becoming hypochromatic.
2.80 % Alcohol 2 minutes 15. Orange G Stain 3 minutes
| Step | Reagent | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 90% Alcohol (Fixation) | 15-30 minutes |
| 3. | 60% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 4. | Distilled Water | 5 dips |
| 5. | Distilled Water | 5 dips |
| 6. | Hematoxylin stain | 3 minutes |
| 7. | Distilled Water | 10 seconds |
| 8. | 1% Acid Alcohol | 10 seconds (1 dip) |
| 9. | Distilled Water | 10 seconds |
| 10. | Scott’s Tap Water | 2-3 minutes |
| 11. | Running Tap Water | 2 minutes |
| 12. | 60% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 13. | 80% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 14. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 16. | 95% ALcohol | 2 minutes |
| 17. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 18. | Eosin Azure Stain | 3 minutes |
| 19. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 20. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 21. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 22. | 95% Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 23. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 24. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 25. | Absolute Alcohol | 2 minutes |
| 26. | Absolute Alcohol+Xylene (1:1) | 2 minutes |
| 27. | Xylene | 2 minutes |
| 28. | Xylene | 2 minutes |
| 29. | Xylene | Till clear |
| 30. | Mount in D.P.X |
Results and interpretation of Papanicolaou Staining
- Nuclei : Blue
- Acidophilic cells : Red
- Basophilic cells : Blue Green
- Erythrocytes : Orange-red
- Keratin : Orange-red
- Superficial cells : Pink
- Intermediate and Parabasal Cells : Blue Green
- Eosinophil : Orange Red
- Candida : Red
- Trichomonas : Grey green

You should have mentioned the basic system for concluding the results for carcinoma, as its used mainly for cancer diagnosis.
Findings in exfoliative cytology- (5 classes)
Class 1 normal
Class2 atypical
Class 3 intermediate
Class 4 suggestive carcinoma
class 5 positive for cancer.
its awesome article its of benefit to me
Very interested!!!
It’s really interesting and helpful especially to me, I love it.
i like this para. comfort for the staining protocol.
what is the most critical step in the pap staining and why?
mostly to keep it wet this is critical.
If you have all dry cells you will loose all stainig criteria and end up with brown smear and nothing to diagnose.
so you shoul put ur smear in fixative immediately.
Thanks
Please explain pap in rapid method
it was really helpful for me brother
it was really informative and useful.wo
thank you for information
INTERESTED YOUR SITE
BUT PAP STAINING AS WELL AS A LIKE
1-FIX..
2-RUN.. WAT..
3-HEM…
4-RUN.(BLUING)..
5-ACID DIFF..
6-RUN.. WA..
7- OG 6
8- 2 TIME AICOHOL DISSE..
9-EA 36
10-3 TIME ALCOHOL ASSENDI
11-DRY AND DEEP IN XYLINE
12-MOUNT WITH DPX
13-MICROSCOPY
IN OUR LAB IS NOT A LONG PROCESS AND YOUR STAINING METHOD IS LONG
WHY???????
it was useful
Interested material
Best guidance for all students & Dr.
Thank you so much