What are Antigens?
Antigens are substances that trigger the body to cause an immune response. The body perceives antigens as harmful substances and it does its best to eliminate them by producing antibodies.
What antigens do is they activate lymphocytes (white blood cells) responsible for fighting off infection.

Image 1: Antibodies and antigens reacting on each other.
Picture Source: cdn.technologynetworks.com
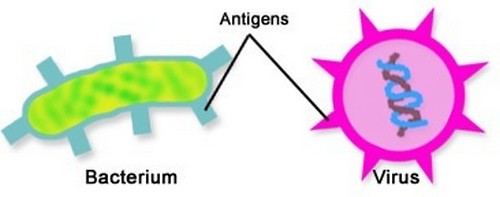
Picture 2: Bacteria and viruses are the two common forms of antigens.
Photo Source: qph.fs.quoracdn.net
Two divisions of antigens
- Foreign antigens (heteroantigens) – These are antigens that originate outside the body such as the ones cause by viruses and other harmful microorganisms like food allergens (certain protein in foods), snake venom, and components of red blood cells from other person.
- Self entigens (autoantigens) – These antigens originate within the body, which is actually the case in patients with autoimmune disorders. (1, 2, 3)
What are antibodies?
Antibodies are also known as immunoglobulins. They are proteins that have a distinct Y shape and are produced by B cells as a result of exposure to antigens.
The antibody has paratope responsible for recognizing a specific epitope of antigen. It is the one responsible for antibody’s lock and key binding action. What antibodies do is they get rid of antigens from the body. (3, 4)

Photo 3: Antibodies work hard to protect the body from infections.
Image Source: std-dwarzbv.netdna-ssl.com

Image 4: Different types of antibodies.
Picture Source: www.assignmentpoint.com
Classes of antibodies
- Immunoglobulin G – It is the most important antibody. It circulates in the bloodstream and other fluids in the body. Thus, protecting the body from bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms.
- Immunoglobulin A – It is an antibody that you can find in the saliva, tears, mucus, respiratory secretions, digestive secretions, as well as secretions of the reproductive system and urinary tract. What it does is it neutralizes the bacteria and viruses thereby preventing these harmful microorganisms from causing harm to the body.
- Immunoglobulin M – It is the largest of all antibodies (consists of five Y-shaped units). It has the same functions as the immunoglobulin G but the only difference is that immunoglobulin M cannot cross the membranes considering its gigantic size.
- Immunoglobulin D and Immunoglobulin E – They are secondary antibodies. Immunoglobulin E is one of the health markers used to detect allergic reaction, infection, malignancy, and other types of inflammatory diseases. (3, 4, 5, 6)

Picture 5: A closer look at the difference between antigen and antibody.
Photo Source: i.ytimg.com
Let us take a look at the differences between antigen and antibody
Definition
- Antigen – A substance that can trigger an immune response.
- Antibody – A type of protein that binds to antigen.
Origin
- Antigen – It can be from external source or within the body.
- Antibody – It is within the body. (7)
Molecular Type
- Antigens – Proteins, lipids, polysaccharides, and nucleic acid.
- Antibody – Proteins (6)
Binding site
- Antigen – Epitope
- Antibody – Paratope
Effects on the body
- Antigen – It causes disease or allergic reaction.
- Antibody – It protects the body from harmful microorganisms.
Importance
- Antigen – It is useful in controlling what goes in and out of the cell.
- Antibody – It is of high importance for without it people will die because of virus attack.(8)
Other names
- Antigen – It is also called immunogens.
- Antibody – It is also called immunoglobulin.
Prevalence
- Antigen – It is found in all types of cells but mostly found in bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Antibody – It is found in some types of cells.
Where can they be found?
- Antigen – Antigens are hook on the cell’s surface and are present in every cell.
- Antibody – Antibodies are found in various parts of the body including the following:
- IgA – It is found in the ears, eyes, vagina, digestive tract, nose, breathing passages, and saliva.
- IgD – It is found on the tissue lining of the chest and abdomen.
- IgG – It is present in all body fluids.
- IgE – It is found in the mucous membranes, lungs, and skin.
- IgM – It is found in the lymph fluid and the blood. (5, 8, 9, 10)
Blood type Antigens and Antibodies chart
Difference between Antigen and Antibody
The medical significance of antibodies test is helpful in various diagnostic procedures. Some of the reasons why a doctor tests your blood for antibodies include the following:
- To detect the presence of allergy or autoimmune disease.
- To check for past and present/current infection.
- To find out if the recurring infection is caused by a low level of immunoglobulin G antibody or other types of immunoglobulins.
- To check for immune response.
- To check on the treatment of cancer such as in the case of a bone marrow.
- To detect a specific type of cancer.
Antibodies and antigens are molecules interconnected with the body’s immune response. An antigen is the one that triggers immune response whereas the antibody is a protein produced in response to an antigen. (12, 13, 14, 15)
| Antigen | Antibody | |
|---|---|---|
| Other names | Immunogens | Immunoglobulins |
| Definition | A substance that trigger an immune response | A type of protein that binds to antigen |
| Origin | Can be found on external source or within the body | Within the body |
| Molecular type | Proteins, lipids, polysaccharides, and nucleic acid. | Proteins |
| Binding site | Epitope | Paratope |
| Effects on the body | It is responsible for causing a disease or an allergic reaction. | It protects the body from harmful microorganisms. |
| Significance/importance | It controls what goes in and out of the cell. | It protects the body from infection, especially in the case of a virus attack. |
| Prevalence | Found in almost all types of cells (bacteria, viruses, and fungi) | Present in some type of cells. (11) |
| Location/Where can they be found? | Antigens are hook on the cell’s surface and are present in every cell. | Antibodies are found in various parts of the body including the following:
|
| Appearance |  |  |
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigen
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/antigen
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibody
- https://www.bio-rad-antibodies.com/immunoglobulin-antibody.html
- https://www.technologynetworks.com/tn/articles/antigen-vs-antibody-what-are-the-differences-293550
- https://www.diffen.com/difference/Antibody_vs_Antigen
- https://www.biologyexams4u.com/2012/11/difference-between-antigen-and-antibody.html
- https://www.bioexplorer.net/differences-between-antibody-and-antigen.html/
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-antigen-and-antibody/
- http://www.scienceclarified.com/Al-As/Antibody-and-Antigen.html
- https://microbiologyonline.org/about-microbiology/microbes-and-the-human-body/antibody-antigen-complex
- http://pediaa.com/difference-between-antigen-and-antibody/
- https://patient.info/health/antibody-and-antigen-tests
- https://microbenotes.com/differences-between-antigen-and-antibody/
- https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/what-relationship-between-antigen-antibody-how-325668

