Urine contains many dissolved substances (solutes) that the body needs to eliminate as waste chemicals. These solutes can form crystals when the concentration of dissolved substances has increased or when the pH level is increasing in either acid or base.
This condition of presence of crystals in the urine is known as crystalluria. Sometimes crystals are found in healthy people and other times they are indicators of organ dysfunction, the presence of urinary tract stones of a like composition (known as urolithiasis), or an infection in the urinary tract.
| Normal Crystals | Abnormal Crystals |
|---|---|
| 1. Uric acid Crystals | 1. Bilirubin Crystals |
| 2. Calcium Oxalate Crystals | 2. Cholesterol Crystals |
| 3. Hippuric Crystals | 3. Cysteine Crystals |
| 4. Calcium Phosphate Crystals | 4. Leucine Crystals |
| 5. Triple Phosphate Crystals | 5. Tyrosine Crystals |
| 6. Calcium Carbonate Crystals | 6. Sulfa Crystals |
| 7. Ammonium Biurate Crystals | 8. Indinavir Crystals |
Crystals that are Normal in Urine
Uric acid Crystals
Uric acid crystals are of varying sizes and shapes, found in acidic urine. They resemble rhomboids, parallelograms, and rosettes in shape and are amber in color. Though they are seen in normal urine, are also an indicator of disease processes, such as acute uric acid nephropathy or urate nephrolithiasis.
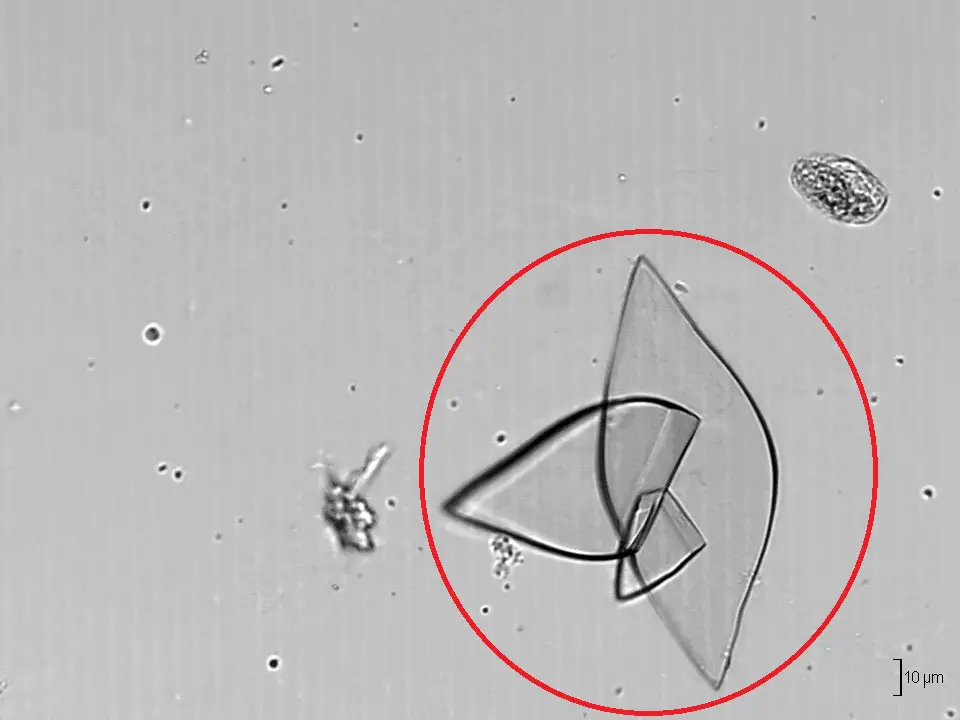
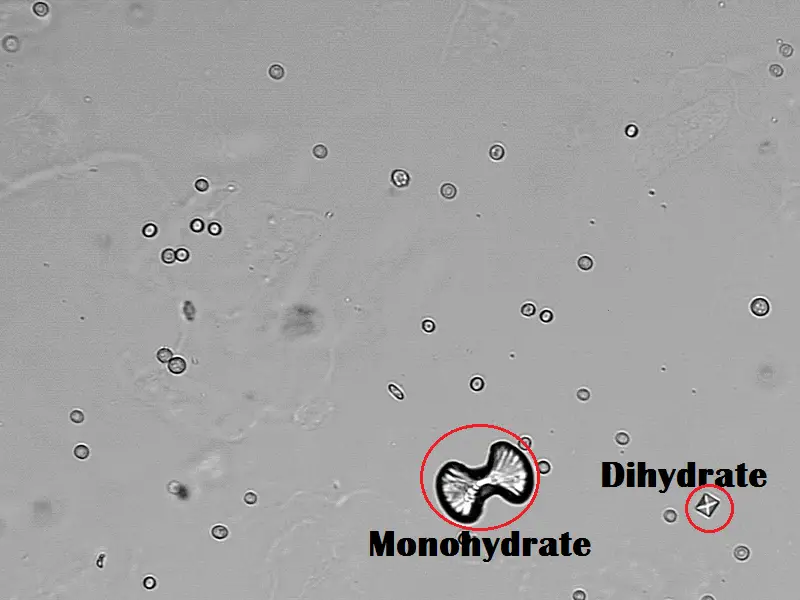
Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Calcium oxalate crystals are found in individuals with acidic, neutral or alkaline urine. These crystals are colorless when viewed microscopically. There are two forms of the calcium oxalate crystal: the monohydrate and dihydrate form.
The monohydrate calcium oxalate crystal is described as the “picket fence” form. These dumbbells shaped crystals are common in ethylene glycol toxicity. The dihydrate form is octahedral or “envelope” shaped.
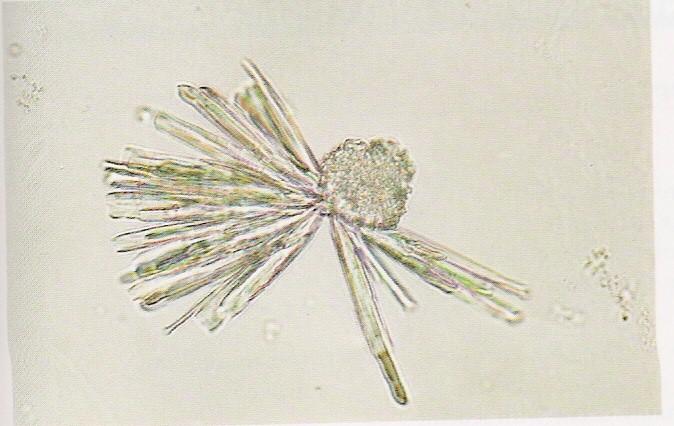
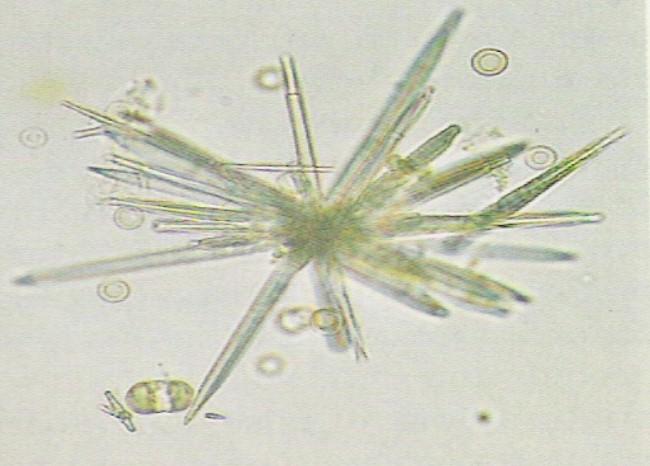
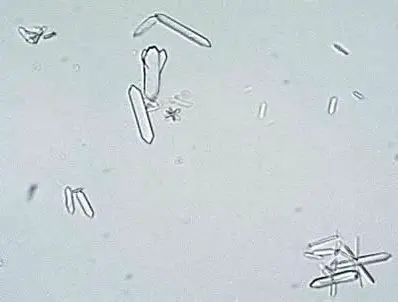
Hippuric acid Crystals
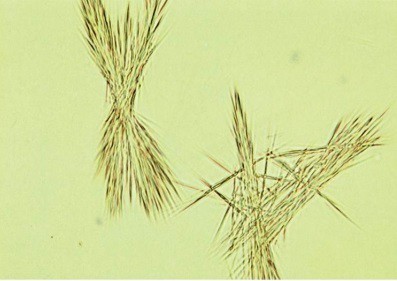
Hippuric acid crystals are found in acid, neutral, or slightly alkaline urine. These colorless crystals are prisms, plates, or needle-like in shape. These crystals are often conglomerated into masses.
Triple Phosphate Crystals or struvite
Triple phosphate crystals form in alkaline urine and are composed of magnesium, ammonium and phosphate. These are rectangular in shape or similar with the coffin lid. These are sometimes associated with a bacterial urinary tract infection caused by urea splitting bacteria.
Calcium Carbonate Crystals
Calcium carbonate crystals are yellow to colorless dumbells or spheres with radial striations, found in alkaline urine. They are usually large crystals and can be readily observed at low magnification.
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
These are colorless crystals having shape like blunt ended needles or prisms, rosettes. These crystals are found in neutral to alkaline pH.
Ammonium Biurate Crystals
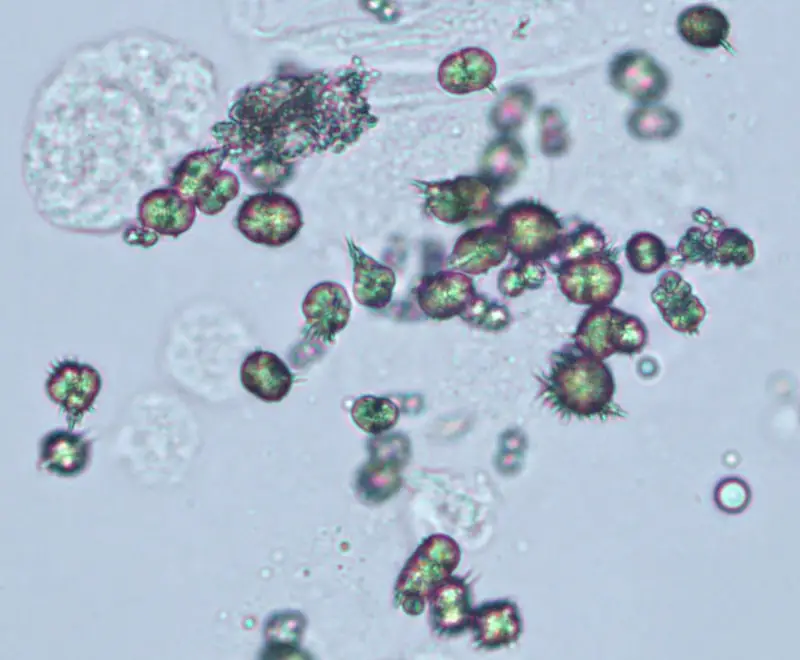
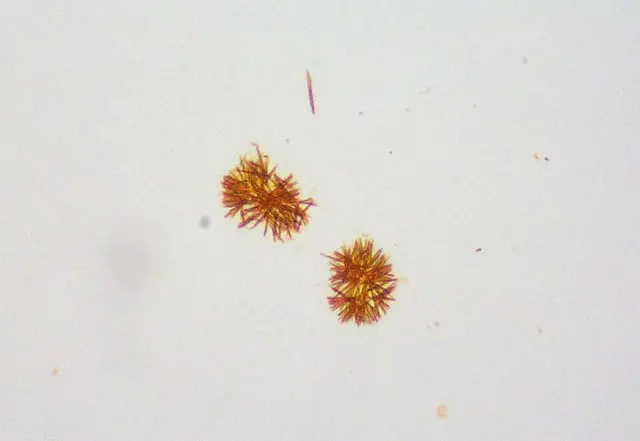
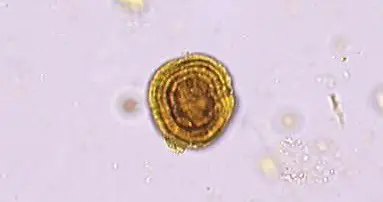
Ammonium urate (or biurate) crystals generally appear as brown or yellow-brown spherical bodies with irregular protrusions resembling “throny-apples”. These are found in alkaline urine.
Amorphous Crystals
Amorphous urates are found in acid urine. These crystals may appear pink on gross analysis and yellow microscopically. These crystals appear as granules in the urine sediment.
Amorphous phosphates are found in alkaline urine. These granules are colorless microscopically.
Crystals that are abnormal in Urine
Bilirubin crystals
Bilirubin crystals are abnormal crystals in urine. They form from conjugated bilirubin and are needle-like to granular crystals that are yellow in color.
They are frequently attached to the surface of cells. Bilirubin crystals are seen in several hepatic disorders.
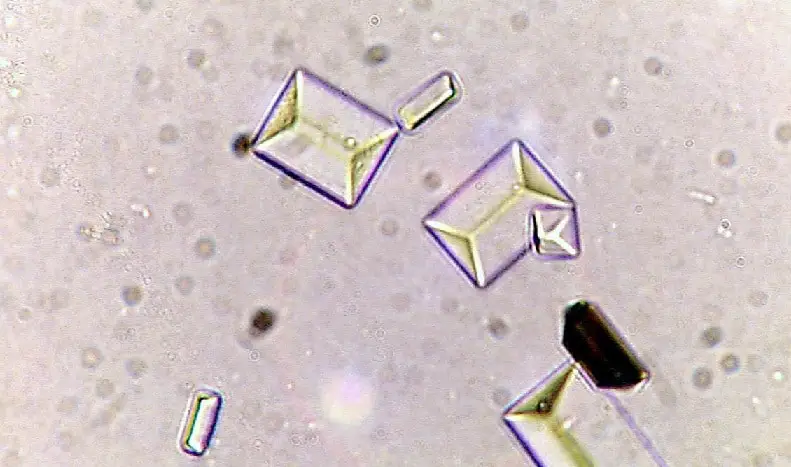
Cholesterol Crystals
These appear as colorless rectangular plates with a notch in one or more corners and are found in acidic urine. The appearance of cholesterol is associated with the Nephrotic Syndrome.
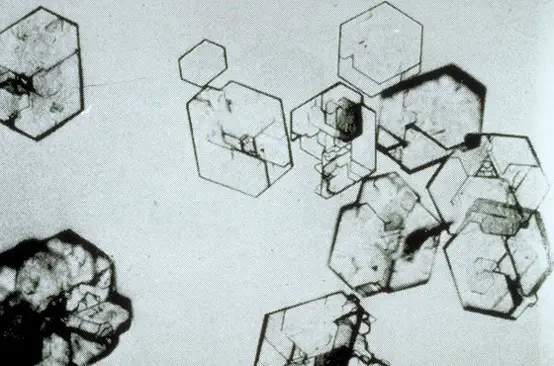
Cysteine Crystals
Cystine crystals are flat colorless plates and have a characteristic hexagonal shape with equal or unequal sides.
They occur in acidic urine that are associated with an inherited disorder. Presence of cystine crystals represents a proximal tubular defect in amino acid reabsorption.
Leucine Crystals
These are Yellowish-brown spheres with concentric circles with radial striations found in acidic/neutral urine. Leucine crystals may be seen in liver disorders in which amino acid metabolism is impaired.
Tyrosine Crystals
Tyrosine crystals appear as colorless/yellow fine needles in acidic/neutral urine. Tyrosine crystals may be seen in tyrosinemia and in certain liver disorders in which amino acid metabolism is impaired.
Sulfanomide Crystals
These are flat needles, sheaves of small needles or as spheroids. Often brown in color. The presence of sulfanomide crystals usually indicates administration of the drug and not necessarily a pathological condition.
However, their presence is also associated with kidney stone formation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What does it mean to have crystals in your urine?
Q 2. How do you treat crystals in urine?
Q 3. How can you tell if urine has crystals?
1. Cloudy and foul-smelling urine
2. Presence of blood in the urine leading to changes in urine color – brownish, pinkish, to reddish
3. Nausea and vomiting
4. Urgency to urinate and painful urination
5. Flank pain
Q 4. How can you tell if urine has crystals?
Q 5. How do you prevent crystals in urine?
1. Drinking plenty of fluids approximately 2.5 liters of water/day.
2. Limit your intake of foods high in sodium (salt) as they can increase the amount of calcium in urine, which eventually leads to stone formation.
3. Be conscious of your protein intake as such can greatly increase the formation of the stone.
4. Make sure you take the right amount of calcium.
5. Limit your intake of high oxalate foods such as soy products, beets, bran, and nuts.
Q 6. Do crystals in urine mean kidney stones?
Q 7. What causes amorphous crystals in urine?
Q 8. What is the best drink to flush your kidneys?
Q 9. What type of crystals are found in diabetic urine?
Q 10. How do you reduce amorphous Urates in urine?
Q 11. What do ketones in urine look like?
Q 12. What does protein in urine look like?
Q 13. What are the worst foods for kidney stones?
Q 14. What causes urate crystals?
Q 15. Can humans get crystals in their urine?
Q 16. What color is urine when your kidneys are failing?
Q 17. What causes smelly urine in a woman?
Q 18. What does diabetic urine smell like?
Q 19. What are the signs that something is wrong with your kidneys?
– Painful urination
– Dramatic changes in urinating habits, especially in quantity and urgency.
– Foamy, discolored, and bloody urine
– A feeling of fatigue
– Swelling that is noticeable around the eyes, face, abdomen, arms, and legs.
– Flank pain
– Joint pain/bone pain





good
Thank u so much DHURBA..this helped me a lot.
Thank you.
thNx durbs
Thank you Dhurba!! I am studying for the DHA exam for laboratory technician and i found this website so helpful!!! Thanks a lot!!!
Thanks! Dhurba. it’s nice, short and precise valuable information.
That is very useful letter. Thanks
Hi
Refreshing
superb.and moreover the important fundamental to be known. And .also post regarding the coombs test was also informative. And im more curious towards the next one
very interested website
why some crystals is not belong a disease?
The immages are clear and the facts are precise
smart work very nice sometimes we forget these things
Thank u for this post…it’s an organized presentation with prominent pics.
great reference to an organized urine sediment
Thanks bro
thanx
it helped me
Very good write-up,Dhruv.Hoping to read a lot more on this pages.Kudos!!??
Nice one. Thanks.
It helped a lot
This is amazing and beautiful! Thank you for putting together these photos, I’ve shared on twitter 🙂
Great minds great people. Keep up the good work
Thank you very much!!
that is great things for us
best note
Fantastic resource
-PA Student, 2nd year.
Hi
Interesting
Informative, helpfull
Thank you for the wonderful photos and notes! You have helped
so many their studies and work!
about good knowledge.lot thanks. we all updated news