Rheumatoid Factors (RF) are autoantibodies that react with individuals own immunoglobulin. These antibodies are usually directed against the Fc fragment of the human IgG.
RF have been associated with three major immunoglobulin classes: IgM, IgG, and IgA. Of these IgM and IgG are the most common. The formation of immune complex in the joint space leads to the activation of complement and destructive inflammation, causing rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
As indicated by its name, RF has particular application to diagnosis and monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting primarily the joints and periarticular tissues. Rheumatoid factor is detected in 60-80% of cases of diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis.
However, it is also detectable sometimes in the serum of patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and in certain non-rheumatic conditions. Elevated values may also be observed in normal elderly population.
Principle of RF test
A number of methods are available for testing of RF. The most commonly used serological method is based on latex agglutination test. As RF is an IgM class of antibody directed against the Fc portion of the IgG molecule, it is detected by it’s ability to agglutinate the latex particles coated with IgG molecule.
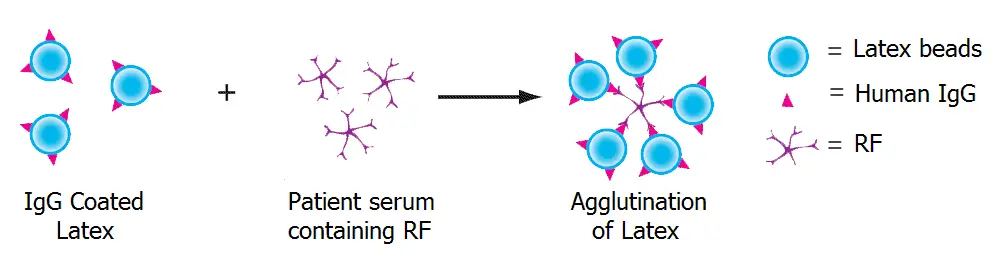
Reagent used is a suspension of polystyrene latex particles in glycine-saline buffer with pH: 8.6 ± 0.1, coated with human gamma globulin.
Qualitative method
Procedure
- Bring all reagents and specimens to room temperature.
- Place one drop of the positive control and 40ul of the patient serum into separate circles on the slide.
- Gently and add one drop of RF latex reagent on each circle of sample to be tested and control.
- Use separate Applicator sticks/stir sticks to spread reaction mixture over entire area of the particular field.
- Tilt the slide back and forth for 2 minutes in a rotary shaker so that the mixture rotates slowly.
- Observe for agglutination after 2 minutes under bright artificial light.
Interpretation
Agglutination of latex particles is considered a positive reaction, indicating the presence of rheumatoid factor at a significant and detectable level.
Positive result: An agglutination of the latex particles suspension will occur within two minutes, indicating a RF level of more than 18 IU/ml.
Negative result: No agglutination of the latex particles suspension within two minutes.
Semi-quantitative method
- Using isotonic saline prepare serial dilutions of the test sample positive in the qualitative method 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16,1:32, 1:64, 1:128 and so on as follows :
- For each specimen to be tested, add 100 µL of 0.9% saline into test tubes numbered 1 to 5.
- Add 100 µL of specimen onto test tube 1.
- Mix the mixture. Avoid formation of bubbles.
- Transfer 100 µL of mixed sample from tube 1 to 2.
- Repeat this serial dilution procedure in tube 3 to 4, and then 5. Dispose 100 µL from test tube 5 after mixing
- Tubes 1 to 5 now represent a dilution series as follows:
Tube Number 1 2 3 4 5 Dilution 1:2 1:4 1:8 1:16 1:32
- Perform the qualitative test procedure using each dilution as test specimen.
Interpretation
The titre is reported as the reciprocal of the highest dilution, which shows a positive test result. Read the titre in the last dilution step with visible agglutination and the approximate concentration of the rheumatoid factor can be determined as follows:
RF in IU/mL= Sensitivity of latex Gammaglobulin reagent in IU/mL × Titre.
Limitations of RF test
- RF is not detected in all patients diagnosed with RA.
- RF may be detected in increased amounts in patients with infectious mononucleosis, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, TB or leprosy, and other conditions of acute or chronic immune response.
- The significance of a positive result should be interpreted with caution. Quantitative testing should be done to confirm diagnosis of RA.
- Highly haemolyzed and lipemic serum as well as plasma interfere with the test.

I’m a medical lab technologist