The motility of bacteria is used to differentiate and classify them. There are many different ways to check for bacteria motility such as the usual microscopic visualization in conjunction with media results and biochemical tests. A bacterium moves using flagella while some move using axial filaments.
Bacteria are classified into two: motile and non-motile. A motile bacteria have the ability to move in the surrounding medium while non-motile do not have the ability to move in the surrounding medium. (1, 2, and 3)

Picture 1: Three test tubes test for bacterial motility.
Image Source: microbeonline.com
What is the purpose of a motility test?
The purpose of a motility test is to check whether bacteria can swim by means of flagella. It is important as not all bacteria with flagella can swim.
Motility test medium
- Beef extract
- Sodium chloride
- Pancreatic digest of casein
- Agar (2, 3)
Procedure
- Boil a liter of distilled water to melt agar.
- Add at least 1% of TTC solution.
- Get 5ml aliquots into the tube and autoclave at a temperature of 121 degree Celsius for about 15 minutes.
- Once inoculation is complete, incubate for 18 hours at 35 degree Celsius until growth is evident. (3, 4, and 5)
Note:
Most biological supply companies sell commercially available premixed forms of the motility test medium.
What to keep in mind?
- Use a sterile needle to pick an isolated colony of bacteria.
- Stab the medium to within 1 cm of the bottom of the test tube.
- Incubate for 18 hours at 35 degree Celsius.
Result
- Positive – The test is positive if there is a red turbid area that extends away from the inoculation line.
- Negative – The test is negative if there is a red growth along the inoculation line but does not extend away.
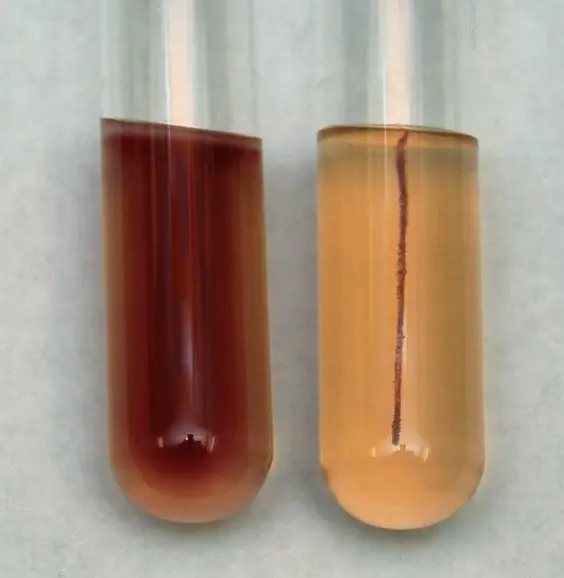

Picture 2: The test tube on the left is positive for motility test while the test tube on the right tests negative.
Image Source: asmscience.org
Other methods to test for motility
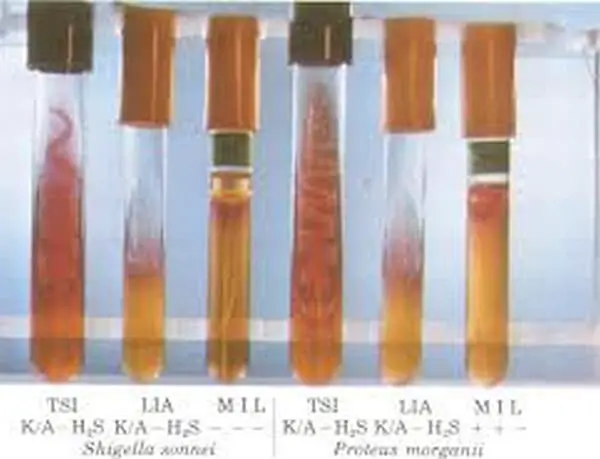

Picture 3: Motility test using the MIL medium.
Image Source: gstatic.com
#1 Motility-indole-lysine (MIL) medium
Ingredients:
- Peptone
- Tryptone
- Dextrose
- L-lysine hydrochloride
- Yeast extract
- Ferric ammonium citrate
- Agar
- Bromcresol purple
Procedure
- Dissolve the agar by boiling a liter of distilled water.
- Dispense 5ml aliquots in a test tube.
- Autoclave for 15 minutes at 121 degree Celsius under 15 psi pressure.
- Check for motility by using a sterile needle.
- Pick an isolated colony and stab the medium to within 1 cm of the bottom of the test tube.
- Incubate for 18 hours at 35 degree Celsius or until such time that growth is noticeable. (4, 5, and 6)
Results
Positive – A diffuse cloud of growth away from the inoculation line is evident. What is good about this procedure is it does not only check for bacteria’s motility, but it also helps determine other metabolic characteristics. (4, 5)
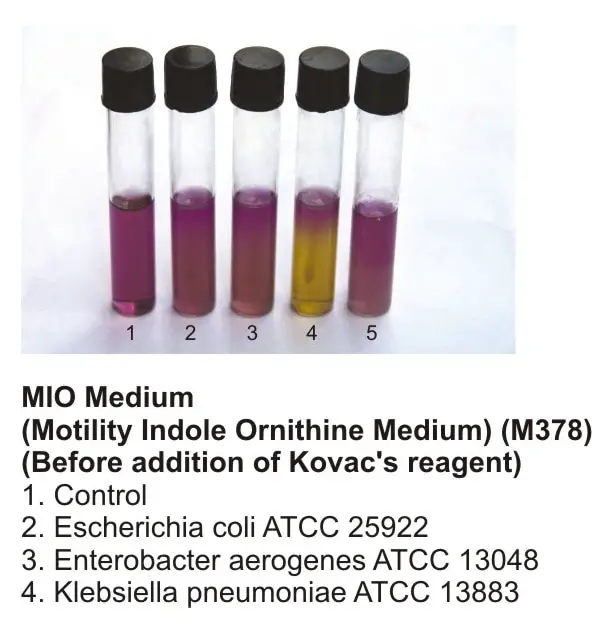
Picture 4: Motility test using the MIO medium.
Image Source: himedialabs.com
#2 Motility-indole-ornithine (MIO) medium
Ingredients
- Yeast extract
- Tryptone
- Peptone
- Dextrose
- L-ornithine HCl
- Bromcresol purple
- Agar
Procedure
- Dissolve agar by bringing to boil a liter of distilled water.
- Dispense 5ml aliquots in a test tube.
- Autoclave for 15 minutes at 121°C under 15 psi pressure.
- Use a sterile needle to collect an isolated colony of bacteria.
- Stab the medium to within 1 cm of the bottom of the test tube.
- See to it that the needle is aligned as it is inserted and removed from the medium.
- Incubate for at least 18 hours at 35 degree Celsius or until such time that growth is noticeable. (5, 6, and 7)
Results
The test is positive if a diffuse cloud is formed away from the inoculation line. This type of bacteria motility test does not only determine the motility of bacteria but also determines other metabolic characteristics of bacteria.
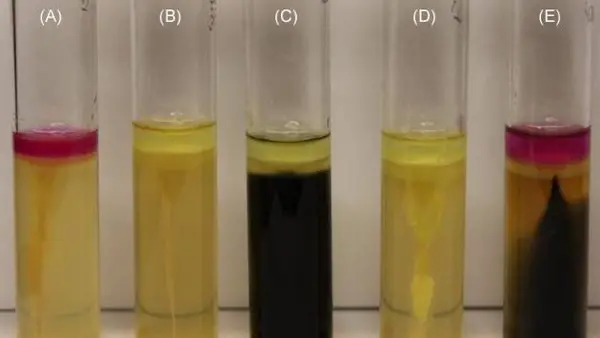
Picture 5: Motility test using the SIM medium.
Image Source: oskinn.com
#3 Sulfide-indole-motility (SIM) medium
Ingredients
- Beef extract
- Peptone
- Agar
- Ferrous ammonium sulphate
- Sodium thiosulfate
Procedures
- Bring to boil a liter of distilled water and dissolve the agar.
- Dispense 5 ml aliquots in a test tube.
- Autoclave for 15 minutes at 121°C under 15 psi pressure.
- Test for motility using a sterile needle. Pick an isolated colony and stab the medium to within 1 cm of the bottom of the test tube.
- Keep the needle in the same line as it is inserted and removed from the medium.
- Incubate for 18 hours at 37 degree Celsius or until you see noticeable growth. (9, 10)
Results
The test is positive if there is a diffuse cloud of growth away from the inoculation line. This procedure does not only check for bacteria’s motility but also other metabolic characteristics.

Picture 5: Motility test using the hanging drop method.
Image Source: slideplayer.com
#4 Hanging drop method
In a wet mount, there is a possibility that the motility of bacteria is hampered. Hence, a hanging drop method is more reliable. Such a method enables you to clearly observe the motility of bacteria including the size and shape.
What is the principle of hanging drop method?
A tiny drop of bacteria is hung from the middle of the cover slip into the cavity slide. It is then observed under the microscope using the oil-immersion objective. The movement in the medium and its surrounding indicates that the bacteria are motile.
On the other hand, if the bacteria remain calm in the medium, it means that the bacteria is non-motile. (1, 4, and 6)
Materials
- Cavity slide
- Coverslip
- Lubricant (petroleum jelly)
- Broth culture of bacteria
- Immersion oil
- Loop
- Microscope
Procedure
- Petroleum jelly is applied around the clean and dry cavity slide.
- The loop is put over the flame and allow to cool. Using the sterilized loop, a bacteria is taken from the broth culture.
- A drop of suspension is put at the coverslip’s center.
- The slide is inverted and put on the coverslip. The two are pressed gently to seal the cavity. Make sure that not a single part touches the drop.
- The slide is inverted so that the drop hangs into the cavity.
- The slide is then clipped to the stage and will be examined under the low power objective of the microscope. (6, 8, and 9)
Result
With the hanging drop method, the bacteria will be checked for its motility, shape, arrangement, and size.
References
- https://microbeonline.com/tests-bacterial-motility-procedure-results/
- http://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=73&sim=697&cnt=1
- http://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=73&sim=697&cnt=2
- http://www.asmscience.org/content/education/protocol/protocol.3658
- https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/Content/hugo/MotilityTestMedia.htm
- https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/docserver/fulltext/micro/22/2/mic-22-2-528.pdf?expires=1549031546&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=86953D0CCD8016C7CF5CC49029754EDA
- http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/experiments/experiment-motility-test-of-a-bacteria-by-hanging-drop-preparation-with-figure-biology/26529
- https://www.slideshare.net/likewhatsoever/activity-2-determination-of-bacterial-motility-56870098
- http://www.vumicro.com/vumie/help/VUMICRO/Motility_Test.htm
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167931709007357
