Mayer’s Test was first given by a German Chemist, Julius Robert von Mayer (1814-1878). This test detects alkaloids in the given sample from natural products.
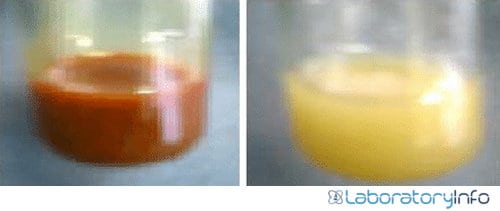
The reaction between Mayer’s reagent and alkaloid and formation of coordinate covalent bond results in cream-colored precipitates.
What are Alkaloids
Alkaloids are essential organic compounds that occur naturally in plants and animals and contain a minimum of one nitrogen atom in their structure. Common examples of Alkaloids are morphine, quinine, nicotine and so on.
Principle of Mayer’s Test
- Mayer’s reagent is used in this test to detect the presence of alkaloids. It is prepared by dissolving mercuric chloride and potassium iodide in water.
- A complex is formed between alkaloid and Mayer’s reagent in Mayer’s Test.
- The nitrogen atom in the alkaloids has a lone pair of electrons that facilitates the formation of a coordinate covalent bond with a metal ion.
- In this case, the nitrogen atom of alkaloid forms a coordinate covalent bond with the potassium ion of Mayer’s reagent, also known as potassium tetraiodomercurate.
- A cream-colored complex is created that appears in the form of precipitates. Precipitate formation confirms the presence of alkaloid in the sample.
Laboratory Requirements for Mayer’s Test
Following are some of the materials and reagent required for performing Mayer’s Test.
Apparatus used
- Test Tubes
- Test Tube Holders
- Test Tube Stand
- Weighing Balance
Required Chemicals
- Potassium Iodide
- Mercuric Chloride
- Distilled Water
- Plant Sample
Preparation of Mayer’s reagent (Formula)
Mix 1.3 grams of mercuric chloride and 5 grams of potassium iodide by weighing it on a weighing balance. Dissolve it in enough distilled water to make the total volume up to 100ml. Mix properly to form a uniform solution.

Protocol
- Take 1ml of plant extract in a test tube.
- Add 1ml of potassium mercuric iodide solution (Mayer’s reagent) to this test tube.
- Shake gently to mix correctly.
- Observe the formation of precipitates in the test tube.
Interpretation of results
- The formation of precipitates of cream color in the test tube will indicate a positive result. Thus, alkaloids are present in the given plant sample.
- No precipitate formation indicates the absence of alkaloids in the test sample.
Benefits of Mayer’s Test
- This test is easier to perform by using a smaller number of reagents and equipment.
- It is used to detect alkaloids in the sample from plants or animal for further usage, mainly in pharmaceutical companies.
Precautions
- The area where the test is performed must be appropriately ventilated.
- Use foam, dry powder, water spray, or clay for cleaning up this chemical in the case of spilling.
- Wash hands immediately after performing Mayer’s Test.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the effects of Alkaloids?
Q2. What are the sources of Alkaloids?
Q3. What are some other tests for the detection of Alkaloids?
1. Dragendorff’s Test
2. Wagner’s Test
3. Marme’ Test
Q4. What do you mean by Alkaloid poisoning?
Q5. Which alkaloid is used as an anesthetic reagent?
Q6. What is the result of Mayer’s Test?
References
- https://media.neliti.com/preliminary-phytochemical-screening-qual-f501b8b2.pdf
- http://new.ijlbpr.com/jlbpradmin/upload/ijlbpr_51d44e989b00d.pdf
- https://www.slideshare.net/alexmpharm/alkaloids-134426257
- https://noteshippo.com/mayers-alkaloids-detection-test-principle-reagents-and-procedure/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mayer%27s_reagent
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail
