In this article we covered information on differences between DNA and RNA. Also please see the bottom of the article for the detailed explanation.
The table below shows the differences between DNA and RNA.
| Points of comparison | DNA | RNA |
| Meaning | Deoxyribonucleic acid | Ribonucleic acid |
| Location | Primarily located in the nucleus although a few can be found in mitochondria | It forms in the nucleolus and moves to the region of cytoplasm |
| Functions |
|
|
| Structure | B-form double helix; a molecule (double-stranded) made up of long-chain nucleotides (4, 5) | A-form helix; a single-stranded helix made up of short-chain of nucleotides. |
| Propagation | Self-replicating | Synthesized from DNA |
| Susceptibility to ultraviolet damage | It is susceptible to ultraviolet damage | It is quite resistant to ultraviolet damage |
| Length | A longer polymer compared to RNA | Vary in length but is usually shorter than the DNA |
| Bases and bases pair |
|
|
| Ability to leave the nucleus | It cannot leave the nucleus | It is capable of leaving the nucleus (8) |
| Quantity | Fixed | Varies |
| Life expectancy | Long-lived | Short-lived |
DNA
Living things like human and animal have DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), a molecule containing the organism’s instructions to develop, grow, live, and reproduce. Every cell contains DNA and the same DNA is passed down from parents to their offspring. (1, 2)

Image 1: DNA is a double helix structure formed by base pair that is attached to the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Picture Source: ghr.nlm.nih.gov

Image 2: DNA is found inside the nucleus of the cell and enveloped in a chromosome to protect from damage.
Picture Source: wikimedia.org
Let us take a look at the DNA structure
DNA contains nucleotides and each nucleotide has a phosphate group made up of sugar and nitrogen base. There are four nitrogen bases:
- Adenine
- Thymine
- Guanine
- Cytosine
The order of the bases is important as they determine the genetic code or instructions of the DNA. According to the United States National Library of Medicine, DNA has around 3 billion bases and 99% are the same in all people. On the other hand, the order of nitrogen bases in the DNA sequence forms the genes. Genes are important as they instruct the cells on how to create proteins.
Nucleotides form two long strands (spiral) by attaching together. The structure is called a double helix. As with the size of the DNA molecule, it is extra-long that it can’t fit into the cell without the appropriate packaging. DNA is tightly coiled to form chromosomes.
That way, it perfectly fits inside the cell. A chromosome contains a single DNA molecule. Human beings have a total of 23 pair of chromosomes. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
History
It was Frederich Miescher; a German biochemist who discovered DNA in 1869. Back then, many researchers don’t realize the significance of DNA. It was in 1953 when the true importance of DNA, especially in carrying out biological information was established. (3, 4)
Importance of DNA testing
DNA testing is important as it determines one’s heritage and can identify if a person is at risk for certain types of diseases. Some of the importance of DNA testing include:
- Diagnosing genetic disorders.
- Figuring out if the person is a carrier of a genetic mutation that can be passed on to the offspring.
- It plays a vital role in research, especially in the field of medicine, genealogy, agriculture, forensic science, and the likes. (4, 5, and 6)
RNA

Image 3: RNA is a single strand molecule available in different types and shapes.
Picture Source: wikimedia.org

Image 4: A closer look at the RNA structure.
Picture Source: wikimedia.org
It is a primary macromolecule vital for all forms of life. It stands for ribonucleic acid. RNA allows the genetic flow of information in the cells. It begins with DNA and travels through the RNA to proteins. As you know, proteins are important in the cells as they are the workhorses. They make everything possible; from enzymatic activities, structural components, and cell signaling, to name a few.
RNA is the photocopy of the DNA. If a cell needs to produce protein, the protein gene is activated to produce multiple copies of DNA pieces in the form of messenger RNA. It is used to translate genetic codes into protein through the cell’s ribosome; the cell’s protein manufacturing machine.
Hence, what the RNA does is it expands the production quantity of a particular protein at a given time from one gene. RNA also serves as the control point as it regulates the amount and time of protein production. (5, 6, and 7)
The significance of RNA
- It is the DNA’s photocopy.
- It is a coupler between protein building block and genetic code.
- It is a structural component of ribosomes.
- It acts as an enzyme which helps speeds up chemical reactions.
- RNA can also carry viral genetic information.
- It helps regulate cellular processes such as cell division, cell growth, cell aging, and death. (6, 7, and 8)

Image 5: The structural difference between DNA and RNA.
Picture Source: technologynetworks.com
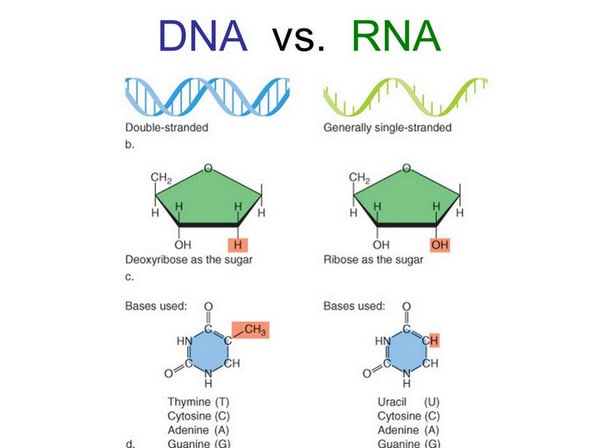
Image 6: The key differences between DNA and RNA.
Picture Source: whatisdna.net
Differences between DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA both play important roles in cellular activities, especially in storing genetic information. They work in synergy but they are totally different entities.
Let us take a look at the primary differences between the two:
DNA
- A complex molecule found in the cell’s nucleus.
- It has a double-helix structure in eukaryotic cells.
- It is present in all living organisms.
- It contains genetic instructions necessary to develop and maintain life.
- Its nucleic acid is deoxyribose.
- Its nucleotides include adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
- It is stable under alkaline conditions.
- Its primary role is to store and transfer genetic information. (8, 9, and 10)
RNA
- Its nucleic acid is ribose.
- It is single-stranded and available in various shapes and types.
- Its molecule can easily fold back on itself because of its single-stranded structure.
- Its nucleotides include uracil, A, G, and C.
- RNA is unstable in alkaline conditions.
- Its primary function is to directly codes for amino acid and serves as a messenger between the DNA and ribosomes to create proteins. (1, 3, and 5)
Which comes first; DNA or RNA?
It is quite difficult to distinguish which comes first. However, many scientists strongly believed that RNA comes first primarily because of its structure. RNA has a simple structure. Without RNA, DNA could not function.
RNA is also present in prokaryotes, which come first before eukaryotes. However, RNA alone could not totally protect the genetic code from damage. Which is why DNA; a double-stranded molecule is needed. (3, 5, and 7)
References
- https://www.sparknotes.com/biology/molecular/structureofnucleicacids/section3/
- https://www.thoughtco.com/dna-versus-rna-608191
- https://www.technologynetworks.com/genomics/lists/what-are-the-key-differences-between-dna-and-rna-296719
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-dna-and-rna/
- https://www.diffen.com/difference/DNA_vs_RNA
- https://biologywise.com/difference-between-dna-rna
- https://cm.jefferson.edu/learn/dna-and-rna/
- http://www.biologydiscussion.com/dna/difference-dna/difference-between-dna-and-rna/12169
- https://sciencing.com/dna-rna-differ-4566205.html
- https://byjus.com/biology/difference-between-dna-and-rna/
