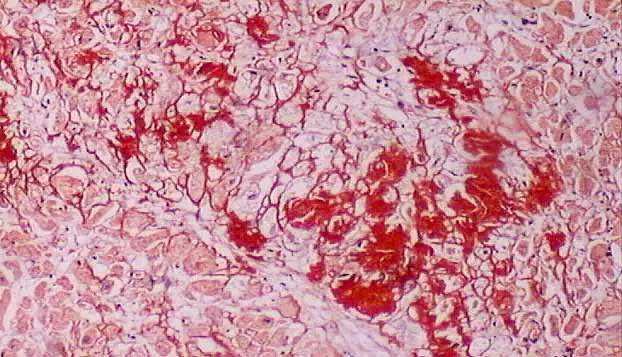
Amyloid refers to the abnormal, fibrous, extracellular proteinaceous deposits found in organs such as liver, kidneys, spleen etc.
This condition of deposition of amyloid in tissues is known as Amyloidosis. Congo red histological staining technique is the gold standard technique for the diagnosis of amyloidosis.
Principle
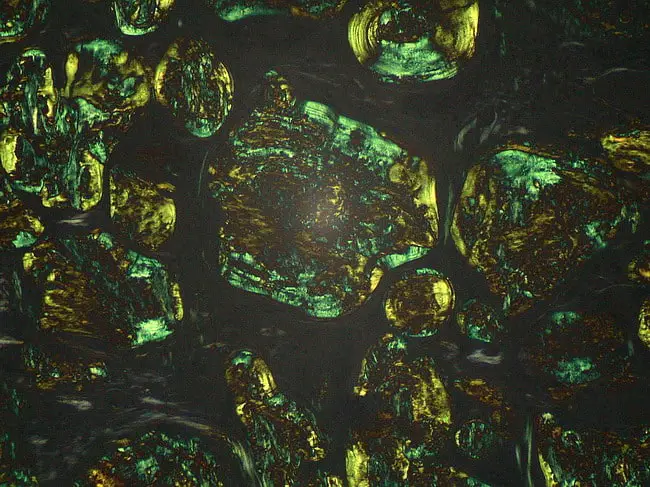
Congo red dye forms nonpolar hydrogen bonds with amyloid and red to apple green birefringence occurs when viewed by polarized light due to alignment of dye molecules on the lineraly arranged amyloid fibrils. The high pH enhances the non-polar hydrogen bonding of congo red and amyloid.
Requirements
- Meyer’s Hematoxylin
- Congo red stock solution
Congo red = 0.3 gm
Sodium Chloride = 0.3 gm
80% alcohol = 100 ml
- NaOH solution
NaOH = 1 gm
Distilled water = 100 ml
- Working congo red
1% NaOH = 0.5 ml
Congo red stock solution = 50 ml
- Alkaline alcohol solution
1% NaOH = 1 ml
50% Alcohol = 100 ml
Procedure
- Deparaffinize and bring sections to distilled water.
- Stain in congo red working solution for 10 minutes.
- Rinse in distilled water.
- Differentiate quickly (9-10 dips) in alkaline alcohol solurion.
- Rinse in tap water.
- Counterstain with Meyer’s Hematoxylin for 30 seconds.
- Dip in ammonia water for 30 seconds until sections turn blue.
- Rinse in distilled water for 10 minutes.
- Dehydrate, clear and mount.
Result and Interpretation
Amyloid : Red to Pink
Nucleus : Blue
In Polarizing Microscope : Red to Green birefringence