Bacteria are the ubiquitous microscopic organisms that are not visible with the naked eye. Bacterial morphology (size, shape and arrangement of bacterial cells) is one of the mostly used feature for the differentiation of various bacterial species.
However pleomorphic bacteria can assume several shapes, following are the three basic bacterial shapes:
- Coccus (plural-cocci) : spherical
- Bacillus (plural-bacilli) : rod-shaped
- Spiral : twisted
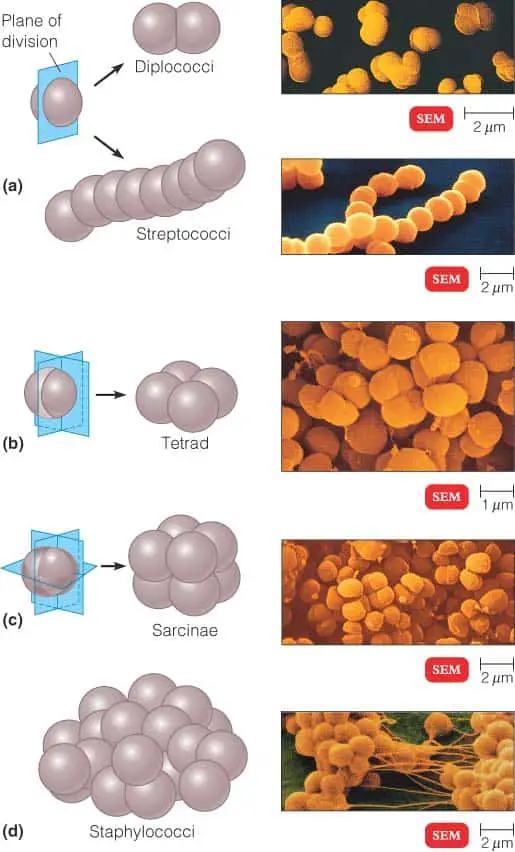
Arrangements of Cocci
- Diplococci : Cocci that remain in pairs after dividing.
- Streptococci : Cocci that remain in chains, like beads on a string.
- Tetrads : The cocci that are arranged in packets of four cells, as the cells divide in two plains.
- Sarcinae : Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight.
- Staphylococci : Cocci that divide in multiple planes and form grape like clusters or sheets.
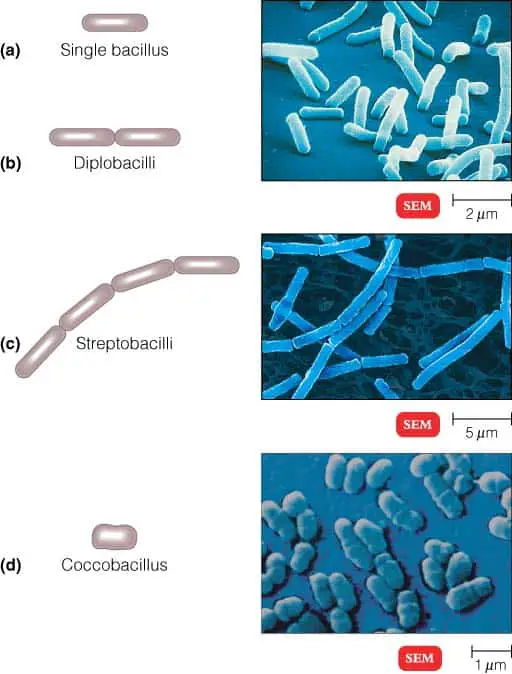
Arrangements of Bacilli (rod shaped bacteria)
- Diplobacilli : Bacilli that remain in pairs after dividing.
- Streptobacilli : Bacilli that remain arranged in end-to-end chains.
- Coccobacilli : Bacilli that are so short and fat which look like cocci.
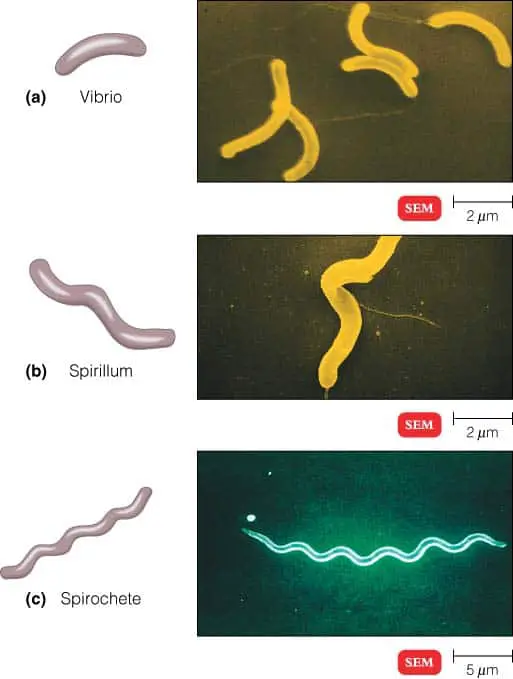
Spiral Bacteria
- Vibrios : Bacteria that are curved or comma-shaped.
- Spirilla : Bacteria that have a helical shape and fairly rigid bodies.
- Spirochetes : Bacteria that have a helical shape and flexible bodies.